Plugin Manager - Packager Help - General Help
This help guide will go through the basic sections in the packager. There is more detail about some of the sections in other help pages.
1. Directories
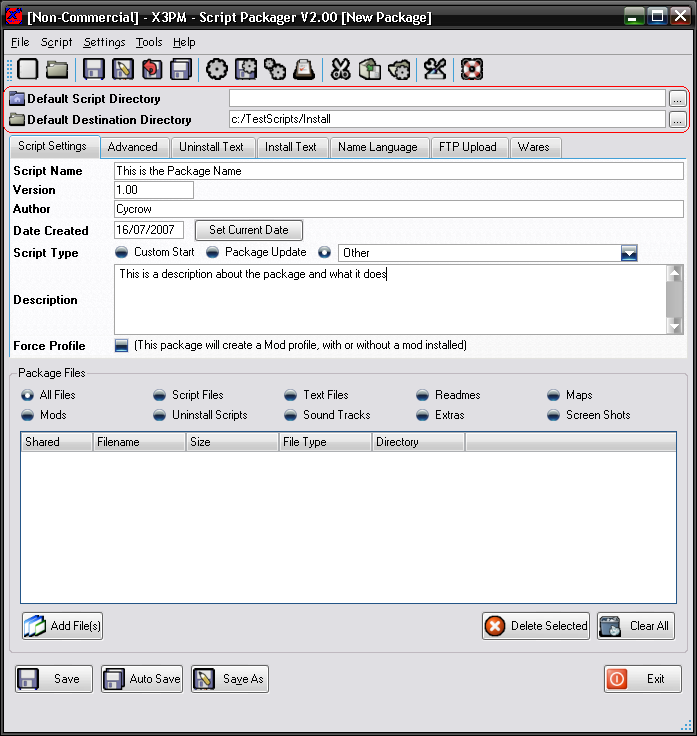
The Directories are found at the top of the dialog. These are used to make it quicker if you have files in certain places.
The first, the Default Script Directory is the directory it will first look when you add any files to the package. If this is set, then the file dialog will automatically default to this when you open it instead of you having to navigate to the same directory each time.
The Default Destination Directory is the directory where you will save or open the SPK files from and will default to this directory. This directory is also used as the $DEFAULTDIR varible in package scripts.
2. Package Settings Tabs
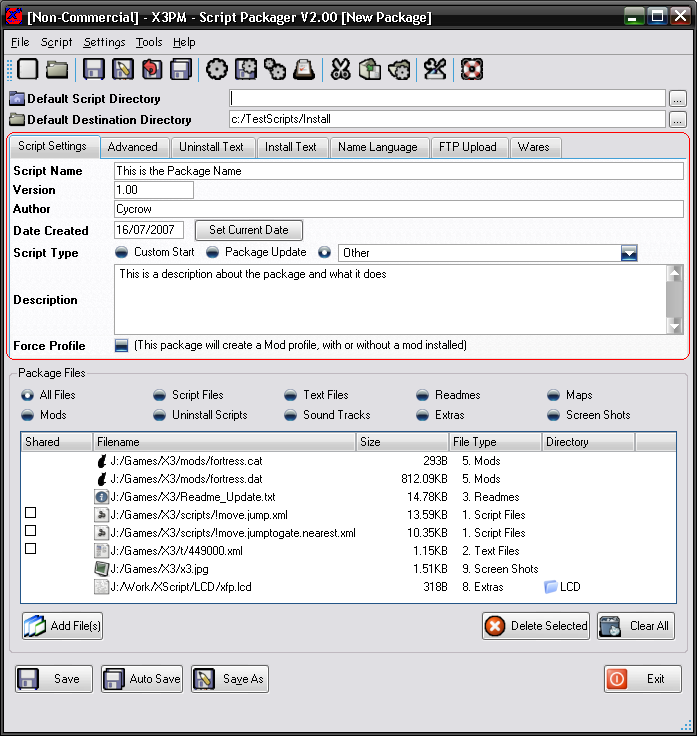
Next, is the settings tabs, these are the various different settings used in the Package file.
- Script Settings: These are the basic settings for the package, most of these will be used in all packages
- Advanced: More advanced settings, these are used to customise the package further
- Uninstall Text: This is custom text that you can display to the user before or after the uninstall process.
- Install Text: Same as the uninstall text, but happens when you install the package.
- Name Language: This allows you to setup the script name in different languages, so it can be displayed in the install list in the correct language.
- FTP Upload: This allows automatic uploading of the file to an FTP Server when you save the package, so it can be ready for hosting
- Wares: This allows you to add custom wares for use with the package.
More detailed help in each section will be found here
3. Files Section
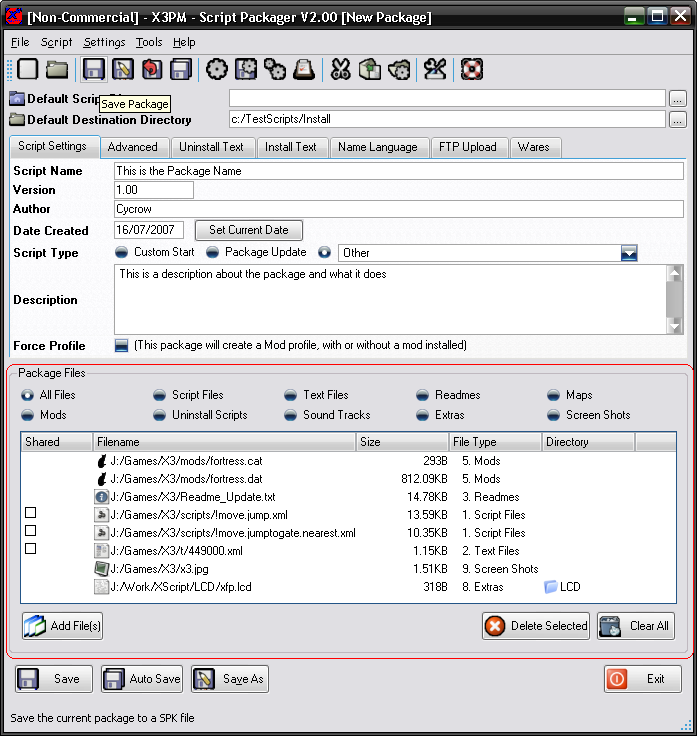
The files section is where you add all the different files into the package. There are several different file types available. The different types determine where they will be installed to.
The "All Files" selection will list all the file types along with what type they add.
To add files simply click on the "Add Files" button to open the file select dialog.
If you have the "All Files" option selected, you will be first presented with a selection of the type of file you wish to add, if you have selected any other file type, it will default to that type and wont ask.
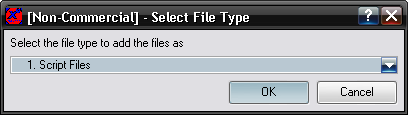
Select the down arrow to select the file type from the list.
In the files dialog you can select the files you wish to add. You can select more than 1 file at a time to add, simply use CRTL and SHIFT to select multiple files at a time.
You can change the filter of the file types by using the bottom drop down box, "Files of Type:". The options that appear here depend on the file type you have selected.
IE, for Scripts, there are 3 options, one for XML files, one for PCK files, and the 3rd to display both.
Once selecting "Open" the files will be added to the list.
You can also drag and drop files from windows explorer into the file list to be added.
To remove files from the list, simply select the files you wish to remove, then click on the "Delete Selected" button. You can select multiple files at a time to delete. The "Clear All" button will delete all files.
Shared Field:
The first field in the list is for the shared files, this is simply a check box. If it is checked then that file type will be a shared file. This means that it will never be removed when uninstalling the package unless the user specifically removes them thierself. This is mainly used if you are using files that are shared with another package that might not be in SPK format. Theres no need to mark them if you are sharing files between different SPK files, as the program will recognise these automatically.
Filename:
This is the filename, will either be the file path to where the file is stored, or will display <PACKAGE>/filename. It displays the package filename when you load the package, and means the file is currently stored in memory.
Size:
The file size is the size of the file when its uncompressed.
File Type:
The file type will only display when you have the "All Files" option and displays the type of file that it currently is. If you select another file type option, then only that file type is displayed in the list, so theres no need for this field.
Directory:
The directory field is only used for 2 file types, the Extra Files and the Readmes. To change it, you simply double click in the field for the file you wish to change. The directory is where the Extra file will be installed to, this can be set to anywhere. If its a readme, then it will be the Language ID of what the ReadMe, this allows the installer to default to certain readmes when set to different languages.
4. File Types
There different files are usually installed in different places and have different operations when they are installed. The file type also determins the valid file extensions that can be used.
- Script Files: These are the main files for scripts, and are installed into the X3/Scripts directory. They are either XML or PCK files. When installing, as well as checking the creation date, they also read the version tags inside the file to find which is the most recent file. The installer will also read the signed tags to see if the script is Signed or not.
- Text Files: Text files are the files that contain the different texts used for the scripts and in the different languages. These are also in XML or PCK format. The text files are installed in the X3/t directory. Any files in this section will be renamed if the option is set in the Installer to match another language. IE, if you add just english text files to the package, the Installer could copy them and rename them to German as well, if the option is set. This allows german versions of the game to have the correct text files as well.
- Readme Files: These are the text files explaining to the user how to use the Package, they are TXT files and can also be in richtext format with some of the basic HTML tags to format the output display. The Readme files can be read directly from the installer and can have a language set so it can default to the correct file.
- Map Files: The map files are installed into the X3/Maps directory, these are the different galaxy maps that you can create, they are also used for Custom Starts. These files will be displayed in the Custom Universe option in game.
- Mod Files: The mod files are the main mod files for the game, these are usually in pairs, with a CAT and a DAT file. You will need both for them to work correctly and can be created using Doubleshadows Mod Manager. These are installed into the X3/Mods directory, and allows the package to have a Mod Profile assigned to it. These can also be automatically selected by X3 if you activate it.
- Fake Patchs: Fake patches are just mod files, they are added to the mod files section like normal, but if you name them as a number, ie 10.cat and 10.dat, they will automatically be recognised as a fake patch. The number of the file doesn't matter as long as its 2 digits. When installing, they will be automatically renamed to fit into the game directory. Unlike mod files, these dont have to be selected to run, so multiple fake patchs can be run. However, higher patchs will override any of the same files in the lower numbers. The cat and dat files much have matching numbers. So you couldn't have 01.cat and 02.dat, the program wont be able to match them up.
- Uninstall Scripts: Uninstall scripts are just normal script files, but instead of being installed in the X3/Scripts directory so the game can use them, they are deactived. They only become active after you uninstall the package. This allows you to do any cleanup like removing wares from stations, unassigned varibles, etc.
- Soundtracks: The sound tracks are MP3 files that are used for the sector music. Usually sound track files will replace any existing ones, so for this type, all original sound track files will first be backed up, so when removing them, the original ones can be restored.
- Extras: Extra files are used to add any files that dont match the other types. These could be manuals in different formats, IE PDF. Or they could be game files that need to be installed in another directory. IE, it could be a new fonts file that needs tobe installed in the X3/types directory.
- Screenshots: The screenshots are the loading screens, whenever you load a game, you will be presented with a loading screen which is basically a picture. You can add your own to the package and it will be picked out at random.





